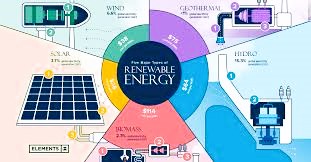
The green energy sector in Nigeria holds immense promise and abundant opportunities. Nigeria’s rich natural resources, encompassing solar, wind, hydro, and biomass, lay a solid groundwork for the expansion of renewable energy. Solar energy, in particular, shines brightly due to Nigeria’s equatorial positioning, ensuring ample sunlight availability.
Despite the nation’s economic growth, a substantial segment of its populace still grapples with the absence of reliable electricity. This energy access disparity unfolds as a vast market waiting to be tapped by investors keen on off-grid and decentralized green energy solutions. Companies specializing in mini-grids and distributed renewable energy systems stand at the threshold of a transformative journey, offering rural electrification and delivering profound social impact.
Economic Growth through Green Investments: Nigeria’s Green Energy Frontier
- Abundant Renewable Resources: Nigeria boasts abundant renewable energy resources, including solar, wind, hydro, and biomass. Solar energy, in particular, has enormous potential given the country’s location near the equator, which results in a high level of solar irradiance.
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Investing in green energy can help Nigeria diversify its energy mix. This is crucial for energy security and reducing dependence on fossil fuels, which are subject to price fluctuations in the global market.
- Energy Access: A significant portion of Nigeria’s population still lacks access to reliable electricity. Green energy solutions, especially off-grid and decentralized systems, can help bridge this energy access gap, offering a substantial market for investors.
- Government Support: The Nigerian government has shown commitment to green energy development through policies, incentives, and regulatory frameworks. Programs like the Nigerian Electrification Project (NEP) and the Rural Electrification Agency (REA) support renewable energy projects.
- Electricity Demand: Nigeria’s electricity demand is expected to grow significantly in the coming years due to population growth and industrialization. Green energy investments can help meet this demand sustainably.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Green energy projects can contribute to reducing Nigeria’s carbon emissions and addressing environmental challenges, such as air pollution and deforestation.
- Investment Incentives: The Nigerian government offers various incentives to attract investors in the green energy sector, including tax breaks, import duty exemptions, and access to concessional financing.
- Technology Adoption: As technology advances and costs decrease, green energy solutions become more cost-effective. Solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems have become more affordable, making green energy investments more attractive.
- Local Job Creation: Green energy projects can create jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and related services, contributing to local economic development.
Clean Energy Financing
Nigeria has made significant progress in securing finance for its energy projects, both domestically and internationally. Various funds have been set aside by governments, institutions, and companies to support the exploration and execution of clean energy initiatives.
In 2020, the European Union committed €30 million ($35.9 million) in funding for renewable energy projects in emerging markets, with a specific focus on financing projects within Nigeria. Managed by the Climate Fund Managers (CFM) in cooperation with the Dutch entrepreneurial development bank FMO, this fund has the potential to unlock €100 million ($119.7 million) in investments for renewable energy projects in Nigeria.
The Green Climate Fund (GCF) has also approved $170.9 million (N70.69 billion) in co-financing for the African Development Bank’s Leveraging Energy Access Finance Framework (LEAF) program in Africa. This program aims to unlock commercial and local-currency financing for decentralized renewable energy projects in Nigeria and other countries, including Ghana, Guinea, Ethiopia, Kenya, and Tunisia.
The Nigerian government has demonstrated its commitment to green energy development. Initiatives like the Nigerian Electrification Project (NEP) and the Rural Electrification Agency (REA) are designed to support renewable energy projects. Additionally, investors can benefit from tax incentives, import duty exemptions, and access to concessional financing.
Conclusion
Nigeria’s green energy potential is a beacon of hope, both for its economic development and environmental preservation. With abundant resources in solar, wind, hydro, biomass, and geothermal energy, Nigeria has the potential to become a trailblazer in Africa’s transition to clean energy. Forward-thinking investors who recognize this potential and are willing to embrace the challenges will not only contribute to Nigeria’s sustainable energy future but also reap substantial rewards from these burgeoning investment opportunities. Green energy is not just an investment; it’s a commitment to empowering Nigeria’s future.