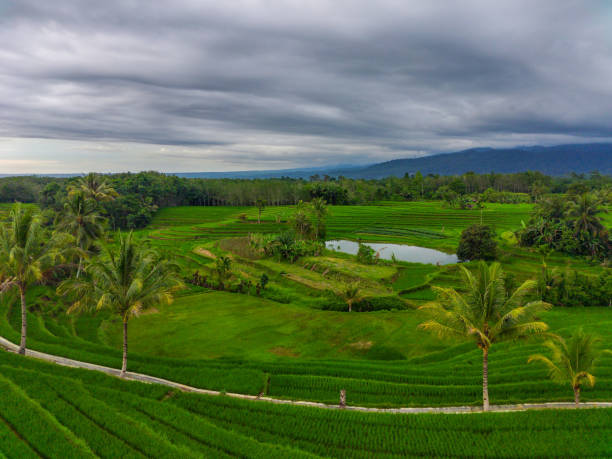
Agrotourism, at its core, is a unique blend of agriculture and tourism. It involves opening up working farms, vineyards, and agricultural facilities to visitors, providing them with an immersive experience in the world of farming and rural life. Unlike traditional tourism, agrotourism aims to connect people with the roots of their food, offering a deeper understanding of the agricultural processes that sustain us.
In recent years, agrotourism has emerged as a significant player in the broader tourism industry. It provides an authentic and enriching alternative to conventional vacations, allowing travellers to escape the hustle and bustle of urban life and connect with nature in a meaningful way. Moreover, agrotourism often fosters a sense of community and cultural exchange, creating memorable experiences for both visitors and hosts.
As of [current year], agrotourism has witnessed a steady rise in popularity across various regions. Farms and agricultural enterprises are diversifying their offerings to cater to a growing demand for authentic rural experiences. From pick-your-own fruit orchards to agrarian bed-and-breakfasts, the range of agrotourism options continues to expand, providing a diverse array of opportunities for travellers seeking a closer connection to the land.
Trends Shaping the Future of Agrotourism
A. Sustainable Practices in Agriculture and Tourism
1. Emphasis on Organic and Local Produce
In the coming years, agrotourism is poised to align more closely with the global shift towards sustainability. Farms and agricultural destinations will increasingly adopt organic farming methods and prioritise the use of local, seasonal produce. This trend not only benefits the environment by reducing the use of synthetic chemicals but also offers visitors a chance to taste fresh, nutrient-rich food straight from the source.
2. Green Initiatives and Eco-Friendly Accommodations
Agrotourism venues will play an active role in environmental conservation. Expect to see an uptick in eco-friendly practices, such as the implementation of renewable energy sources, waste reduction strategies, and the creation of sustainable accommodations like eco-cottages or solar-powered cabins. These initiatives will enhance the overall eco-consciousness of agrotourism experiences.
B. Technological Advancements in Agriculture
1. Smart Farming and Precision Agriculture
The integration of technology into agriculture is set to revolutionise the way farms operate. Smart farming techniques, including sensor-based monitoring, automated irrigation systems, and data-driven crop management, will become commonplace. This not only boosts efficiency but also allows visitors to witness cutting-edge agricultural practices in action.
2. Integration of AI and IoT in Farm Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) will play pivotal roles in optimising farm operations. AI-powered algorithms will analyse vast amounts of agricultural data to make informed decisions, from crop selection to irrigation schedules. Meanwhile, IoT devices will provide real-time insights into soil conditions, weather patterns, and livestock health, creating a more precise and productive farming environment.
C. Personalised Experiences for Visitors
1. Farm-to-Table Dining Experiences
The farm-to-table movement will continue to flourish within the agrotourism sector. Visitors can anticipate immersive culinary experiences, from participating in harvests to learning cooking techniques using fresh, farm-sourced ingredients. This trend not only offers a delectable taste of the local terroir but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the agricultural process.
2. Hands-on Workshops and Activities
Agritourism destinations will increasingly offer hands-on workshops and activities, allowing visitors to actively engage with farm operations. From cheese-making workshops to guided tours of vineyards, these interactive experiences provide a deeper understanding of the labour and expertise that go into producing the goods we often take for granted.
Emerging Destinations for Agritourism
A. Global Expansion of Agrotourism
1. Growth in Developing Countries
Agrotourism is no longer confined to well-established agricultural regions. Developing countries are increasingly recognizing the potential of agrotourism to boost their economies while preserving their agricultural heritage. Expect to see a surge in agrotourism offerings in regions known for their rich agricultural traditions, providing visitors with a unique glimpse into diverse farming practices.
2. Unique Agrotourism Experiences Worldwide
As agrotourism gains traction globally, travellers can anticipate a wider array of unique experiences. From tea plantations in Sri Lanka to saffron farms in Spain, the world is becoming a tapestry of agritourism destinations, each offering its own cultural and agricultural tapestry for visitors to explore.
B. Niche Markets and Specialized Agrotourism Ventures
1. Vineyard Tours and Wine Tourism
Wine tourism, a specialised form of agrotourism, is experiencing a renaissance. Vineyards are increasingly opening their doors to wine enthusiasts, offering guided tours, tastings, and even opportunities to participate in the grape harvest. This niche market caters to those seeking a sophisticated yet down-to-earth agrarian experience.
2. Educational Farm Visits for Students and Families
Agrotourism is also becoming an integral part of educational experiences, particularly for students and families. Farms are transforming into outdoor classrooms, providing hands-on learning opportunities about agriculture, sustainability, and the natural world. These visits not only nurture a love for the land but also instil a sense of responsibility towards the environment.
Challenges and Opportunities in Agrotourism
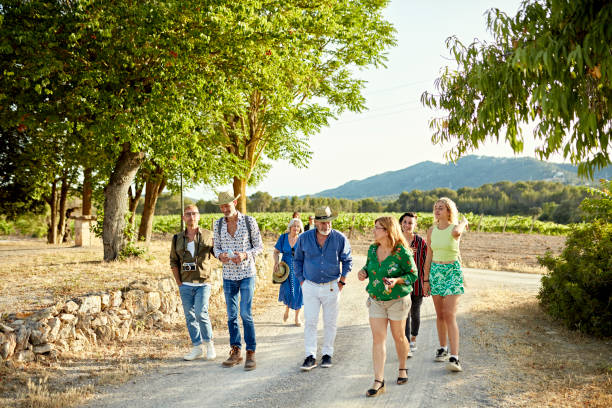

A. Addressing Environmental Concerns
1. Minimising Ecological Footprint
While agrotourism holds great potential, it’s imperative to acknowledge and address its environmental impact. Farms and agro tourism destinations must take proactive steps to minimise their ecological footprint. This includes implementing sustainable farming practices, managing waste responsibly, and conserving natural resources to ensure a harmonious coexistence with the environment.
2. Balancing Tourism with Sustainable Agriculture
Striking a balance between tourism and agriculture is a critical challenge. Agrotourism venues must carefully manage visitor numbers to prevent overburdening the land or disrupting farming operations. Thoughtful planning and sustainable development practices are essential to ensure that agrotourism remains a viable and beneficial endeavour for both the local community and the environment.
B. Regulatory and Policy Considerations
1. Zoning and Land Use Regulations
Navigating zoning laws and land use regulations can be a complex aspect of agritourism development. Farmers and agrotourism operators must work closely with local authorities to ensure compliance with zoning ordinances, especially when incorporating accommodation facilities or expanding visitor offerings. Clear communication and a thorough understanding of local regulations are crucial in this process.
2. Supportive Government Policies for Agritourism
Encouraging governmental policies play a pivotal role in fostering a conducive environment for agritourism. Supportive policies can range from incentives for sustainable practices to streamlined permitting processes. Advocacy for agrotourism at the policy level is essential to create an enabling framework that allows the industry to thrive while adhering to best practices.
Technological Integration in Agrotourism
A. Augmented Reality and Virtual Tours
1. Enhancing Visitor Experience through Technology
As technology continues to advance, agritourism destinations are incorporating augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences to offer visitors a truly immersive encounter with agriculture. Through AR, visitors can interact with digital overlays of farm operations, gaining deeper insights into the processes at play. VR, on the other hand, allows for virtual tours of expansive farms, providing a sense of scale and scope that traditional tours may not capture.
2. Showcasing Agricultural Processes Virtually
For those unable to visit farms in person, virtual tours provide an invaluable opportunity to experience agrotourism from afar. These virtual experiences not only serve as a marketing tool for agritourism destinations but also democratise access, allowing a broader audience to engage with and appreciate the agricultural world.
B. Online Booking Platforms and Reservation Systems
1. Streamlining Visitor Management
The integration of online booking platforms and reservation systems is becoming increasingly prevalent in the agritourism industry. This technology allows farms and agrotourism venues to efficiently manage visitor flow, ensuring that experiences remain enjoyable and personalised. Additionally, it provides a convenient way for visitors to plan their trips and secure their spots in advance.
2. Ensuring Accessibility and Convenience for Guests
By offering online booking options, agritourism destinations enhance accessibility for a diverse range of visitors. Whether planning a family outing or a group excursion, the ease of online reservations simplifies the process and encourages more individuals to partake in agrotourism experiences.
Community and Economic Impact of Agritourism
A. Strengthening Rural Economies
1. Job Creation and Income Generation
Agrotourism has proven to be a boon for rural economies. By opening their doors to visitors, farms and agrotourism ventures create employment opportunities within their communities. This influx of jobs not only supports local livelihoods but also injects economic vitality into rural areas that may have otherwise faced economic challenges.
2. Diversification of Rural Businesses
The presence of agrotourism can stimulate diversification in rural economies. Beyond traditional farming, agritourism destinations may offer additional services such as farm-to-table restaurants, artisanal workshops, or on-site accommodations. This diversification bolsters the resilience of rural communities, reducing their reliance on a single economic sector.
B. Fostering Cultural Exchange and Education
1. Bridging Urban-Rural Divides
Agrotourism facilitates a meaningful exchange between urban and rural communities. Visitors gain a deeper appreciation for the hard work and dedication that goes into agricultural practices, while locals have the opportunity to share their knowledge and passion for the land. This mutual understanding strengthens the bonds between urban and rural populations.
2. Preserving Traditional Agricultural Practices
Agrotourism plays a pivotal role in preserving traditional farming techniques and cultural heritage. As visitors engage with age-old practices, they contribute to the preservation of these methods for future generations. Additionally, the revenue generated from agrotourism can be reinvested in the maintenance and conservation of historical agricultural sites.
Conclusion
In examining the future of agrotourism, it’s clear that this dynamic industry is poised for remarkable growth and transformation. We’ve explored key trends, from sustainable practices and technological integration to emerging destinations and specialised ventures.
As agrotourism continues to evolve, it’s crucial to emphasise sustainability. By adopting eco-friendly initiatives and responsible agricultural practices, we can ensure that agrotourism remains a force for positive change in both the tourism and agricultural sectors.
With its potential to strengthen local economies, bridge urban-rural divides, and preserve cultural heritage, agrotourism holds promise as a vital component of sustainable tourism. As travellers increasingly seek authentic and enriching experiences, the future of agrotourism looks bright.
In the coming years, we can anticipate an even greater fusion of agriculture and tourism, offering visitors a deeper connection to the land and a renewed appreciation for the agricultural roots that sustain us all.